LambdaTest announced its partnership with Assembla, a cloud-based platform for version control and project management.
DevOps and Continuous Delivery are intimately intertwined, both with one another and with revenue growth. In effect, applying DevOps principles across the lifecycle smoothes the way or “greases the wheels” for efficient delivery of application code.
Indeed, in EMA’s latest survey, almost 90% of the respondents reported their companies are utilizing both, and almost 20% are delivering new code daily or more often (see Figure 2). Respondents report business benefits including higher levels of customer satisfaction, faster revenue growth, and better competitive differentiation from their Continuous Delivery initiatives.
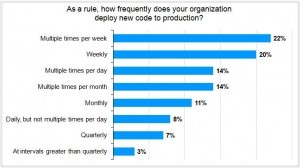
Figure 2. 65% of surveyed companies deliver code at least weekly; 15% deliver daily
There is, however, a dark side to this scenario as well. While the business benefits can be significant, adverse impact on production environments and on IT support can also be significant. Fifty percent of companies surveyed report that development and operations teams are spending more time supporting production as a direct result of frequent production changes. Today, development teams spend approximately as much time supporting production as they do developing new applications. Operations spends almost 15% more time troubleshooting application problems than it does troubleshooting infrastructure problems.
These statistics are a good argument for tools supporting change control, unit and integration testing, workflow management, and deployment automation. They also support investments in Application Performance Management (APM) tools that can be used across the lifecycle to troubleshoot issues in complex application environments.
Increasingly, these high-performing companies are turning to automation to solve these problems. Companies that have automated Continuous Delivery processes often report that production problems decrease, based on the fact that hardware and software provisioning becomes planned and policy-driven, enabling a “cookie cutter” approach. To enable maximum flexibility in terms of deployment targets, best practice dictates that tools supporting deployment, provisioning, workload automation, and release automation should be “cloud ready.”
This means they are equally capable of deploying configurations and code artifacts to cloud infrastructure, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and private cloud environments incorporating virtualization, as they are deploying to traditional physical hardware.
To sum up, the companies growing revenue today appear to be those that are also maximizing investments in DevOps and Continuous Delivery practices and the tools that support them. As the statistics above demonstrate, the results can be stunning. However, automation, properly applied, can mean the difference between applications and services that benefit the business and those that introduce chaos into production and consume additional resources.
Julie Craig is Research Director for Application Management at Enterprise Management Associates (EMA).
Industry News
Salt Security unveiled Salt Illuminate, a platform that redefines how organizations adopt API security.
Workday announced a new unified, AI developer toolset to bring the power of Workday Illuminate directly into the hands of customer and partner developers, enabling them to easily customize and connect AI apps and agents on the Workday platform.
Pegasystems introduced Pega Agentic Process Fabric™, a service that orchestrates all AI agents and systems across an open agentic network for more reliable and accurate automation.
Fivetran announced that its Connector SDK now supports custom connectors for any data source.
Copado announced that Copado Robotic Testing is available in AWS Marketplace, a digital catalog with thousands of software listings from independent software vendors that make it easy to find, test, buy, and deploy software that runs on Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Check Point® Software Technologies Ltd.(link is external) announced major advancements to its family of Quantum Force Security Gateways(link is external).
Sauce Labs announced the general availability of iOS 18 testing on its Virtual Device Cloud (VDC).
Infragistics announced the launch of Infragistics Ultimate 25.1, the company's flagship UX and UI product.
CIQ announced the creation of its Open Source Program Office (OSPO).
Check Point® Software Technologies Ltd.(link is external) announced the launch of its next generation Quantum(link is external) Smart-1 Management Appliances, delivering 2X increase in managed gateways and up to 70% higher log rate, with AI-powered security tools designed to meet the demands of hybrid enterprises.
Salesforce and Informatica have entered into an agreement for Salesforce to acquire Informatica.
Red Hat and Google Cloud announced an expanded collaboration to advance AI for enterprise applications by uniting Red Hat’s open source technologies with Google Cloud’s purpose-built infrastructure and Google’s family of open models, Gemma.
Mirantis announced Mirantis k0rdent Enterprise and Mirantis k0rdent Virtualization, unifying infrastructure for AI, containerized, and VM-based workloads through a Kubernetes-native model, streamlining operations for high-performance AI pipelines, modern microservices, and legacy applications alike.
Snyk launched the Snyk AI Trust Platform, an AI-native agentic platform specifically built to secure and govern software development in the AI Era.












