Backslash Security introduced its Fix Simulation and AI-powered Attack Path Remediation capabilities.
Although DBAs fortunately have the rare ability to bridge the gap between development and operations, they have been detrimentally overlooked in many companies that deploy DevOps practices. A DBA's ability to interrogate code and construct a resilient, well–performing database environment uniquely defines the capabilities needed for DevOps.
Start with DBA: Bridging the Gap Between Development and Operations - Part 1
Reciprocal Teaching
Whether through formal methods such as classroom or virtual training, job shadowing, and mentoring; or through informal methods such as team discussions or presentations, teaching needs to be a frequent element of team integration. It is a given that IT and business teams have difficulty understanding each other without a common taxonomy. Even teams within IT often fail to understand each other.
A developer discussing encapsulation or inheritance may totally perplex a DBA unfamiliar with object-oriented programming terminology. Never mind if you start talking about Agile, which is very new to many IT professionals. Likewise, a DBA ranting about developers "thrashing" the buffer cache is likely to see the "deer in the headlights" stare.
While investigating a performance issue specific to a screen, a developer shared with a DBA that the drop-down window would display ten data elements from which the application user could select. As they looked at the code and then tested the code in a nonprod environment, they learned that the result set was millions of records. The million records would move from the database to the middle tier, and then the needed rows would be pushed to the client application screen. When asking why millions of rows were being returned, the developer said that was a standard practice. After looking into other queries, the DBA soon found herself ranting to several development managers about the developers thrashing the buffer cache and the performance impact. After realizing that these managers did not understand DBA "technical" jargon, she determined that there was a better way to communicate the message. She scheduled a meeting a few days later, in which she put together a presentation deck outlining basic buffer cache concepts with visuals (see Figure 1 ) that demonstrated how large result sets can negatively impact not only the query requesting the data but also every aspect of the database performance.
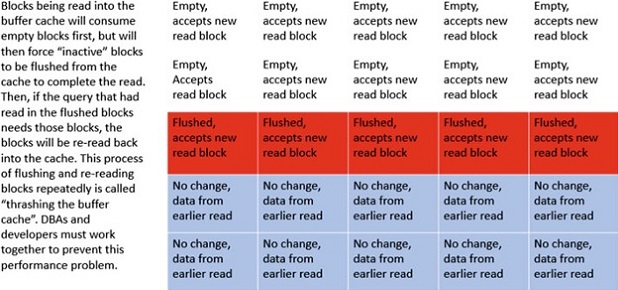
Figure 1. Buffer cache thrashing
After the DBA spent an hour walking the developers through the presentation and answering questions, these developers understood the impact of less-selective queries. As days and weeks passed, and often when the DBA was visiting the developer realm, developers would jokingly remind each other to not thrash that buffer cache unless they wanted the DBA to get after them. Although the training was succinct and simplified, it closed the language gap, resulting in improved query selection criteria, smaller result sets, and less buffer cache "thrashing."
The point is that even people in the same industry do not necessarily speak the same language. DevOps introduces another language gap that requires purposeful definition to keep all members of the team aligned. This book presumes that readers are technically savvy and already familiar with DevOps and the core terminology, but it may not be true as they begin working with DBAs. Accelerating DBA engagement requires DBAs to understand the DevOps principles and foundational constructs.
Experienced DevOps team members need to educate DBAs on processes, continuous integration and delivery, and the implemented tool set. Demonstrating how code is built, tested, integrated, and released helps DBAs determine where best to interject changes supporting the code cycle. DBAs also need early notification when system changes are necessary, allowing time for the reconfiguration to be completed, tested, security approved, and automated for pipeline consumption.
Processes Anew
Differentiating which DBA inputs to put forth for absorption into existing agile and DevOps processes demands collaborative effort between existing team members and newly assigned DBAs. Cohesive integration to advance the undertaking of capturing additional value at decreased costs lengthens the backbone — the code generation process definitions from start to finish — of the movement, triggering existing processes to be rehashed, or repurposed, and then reacclimated within the SDLC cycle.
Together, DBAs and DevOps team members make old things new again as processes throughout the development, testing, release, and operations support pathway are refined to incorporate DBA tools, change methods, and metrics. The critical goal is to not disrupt the code delivery schedule while reaffirming the automation and process sequence preciseness. Sanctioning a parallel environment that initially mirrors the primary build-to-release architecture onto which the DBA components get added enables a side-by-side comparison to ensure that updated processes work correctly. Of course, automation oversees the execution, examination, and effects reporting.
Quick to Value, Delight the Customer
Excitement for DevOps, besides the "it's the cool thing now" factor, stems from years of frustration as IT professionals have been viewed as moneywasting, unresponsive, slow to deliver, and second-rate business citizens. One of my pet peeves has been the "IT alignment to the business" language. Viewing IT as an "outside" entity having to blend in plans to support or conform to the rest of the business accounts for much disillusion and poor esprit de corps.
When agile development (and DevOps in close pursuit) exploded in popularity, IT folks finally envisioned a promising future in which product delivery proficiencies incessantly eliminate time, process, approval, and implementation waste, and then rocket delivery to the customer. One Lean principle is establish pull. Customers establish pull inherently when reporting problems or requesting new product functionality. IT's capability to deliver has never been this radically empowered, in which demand (pull) can be satisfied within a customer's time expectations.
As consolidated teams, call them agile or DevOps, build new or decouple established services from monolithic applications, change footprints become much smaller (think microservices), making it possible to deploy code quickly with minimal risk. With speed united with smaller code chunks, a failed release becomes no more than a temporary blip on the radar.
This blog is an excerpt from Mike Cuppet's book: DevOps, DBAs, and DBaaS
Industry News
Check Point® Software Technologies Ltd. announced the appointment of Nadav Zafrir as Check Point Chief Executive Officer.
Sonatype announced that Sonatype SBOM Manager, its Enterprise-Class Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) solution, and its artifact repository manager, Nexus Repository, are now available in AWS Marketplace, a digital catalog with thousands of software listings from independent software vendors that make it easy to find, test, buy, and deploy software that runs on Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Broadcom unveiled the latest updates to VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF), the company’s flagship private cloud platform.
CAST launched CAST SBOM Manager, a new freemium product designed for product owners, release managers, and compliance specialists.
Zesty announced the launch of its Insights and Automation Platform.
Progress announced the availability of Progress® MarkLogic® FastTrack™, a UI toolkit for building data- and search-driven applications to visually explore complex connected data stored in Progress® MarkLogic® platform.
Snowflake will host the Llama 3.1 collection of multilingual open source large language models (LLMs) in Snowflake Cortex AI for enterprises to easily harness and build powerful AI applications at scale.
Secure Code Warrior announced the availability of SCW Trust Agent – a solution that assesses the specific security competencies of developers for every code commit.
GFT launched AI Impact, a new solution that leverages artificial intelligence to eliminate technical debt, increase developer efficiency and automate critical software development processes.
Code Metal announced a $13M seed, led by Shield Capital.
Atlassian Corporation has achieved Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) “In Process” status and is now listed on the FedRAMP marketplace.
Check Point® Software Technologies Ltd. announced that it has received a Leader ranking in The Forrester Wave™: Mobile Threat Defense Solutions, Q3 2024 report.
Mission Cloud announced the launch of Mission Cloud Engagements - DevOps, a platform designed to transform how businesses manage and execute their AWS DevOps projects.
Accelario announces the release of its free TDM solution, including database virtualization and data anonymization.





